Introduction to Environmental
Accounting
By Rabiu Aminu, PhD, FCNA, FMNES
Environmental accounting also referred to as Green Accounting is a field that identifies resource use, measures and communicates costs of a company’s or national economic impact on the environment. It is a subset of accounting, its target being to incorporate both economic and environmental information. It is a means of integrating environmental considerations into financial decision-making. Therefore, environmental accounting is a vital tool to assist in the management of environmental and operational costs of natural resources.
Environmental accounting is the
practice of incorporating principles of environmental management and
conservation into reporting practices and cost/benefit analyses. It includes
the processing of both financial and nonfinancial information regarding
environmental and ecological impacts.
One of the key principles of
environmental accounting is the concept of "true cost accounting."
This approach involves accounting for all costs associated with a product or
service, including those that are typically externalized, such as pollution or
resource depletion. An environmental accounting system consists of
environmentally differentiated conventional accounting and ecological
accounting. Environmentally differentiated accounting measures effects of the
natural environment on a company in monetary terms.
Classifications of Environmental Accounting
Environmental accounting is
organized in three sub-disciplines: global, national, and corporate
environmental accounting, respectively. Corporate environmental accounting can
be further sub-divided into environmental management accounting and
environmental financial accounting.
The diagram below shows the classifications of environmental accounting.
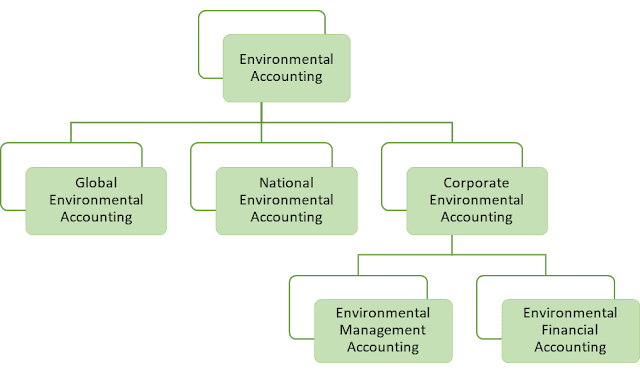 |
| Classifications of Environmental Accounting |
Global Environmental Accounting
Global environmental accounting
is an accounting methodology that deals with energetics, ecology and economics
at a worldwide level. It is a statistical framework that provides a systematic
approach to organizing and analysing environmental and economic data to answer
policy and other questions. The System of Environmental-Economic Accounting
(SEEA) is a framework that integrates economic and environmental data to
provide a more comprehensive and multipurpose view of the interrelationships.
National Environmental Accounting
National environmental accounting
is an accounting approach that deals with economics on a country’s level. It is
a branch of accounting dealing with activities, methods, recordings, analysis,
and reporting of environmental and ecological impacts of defined economic
systems. Internationally, environmental accounting has been formalized into the
System of Integrated Environmental and Economic Accounting, known as SEEA. SEEA
grows out of the System of National Accounts.
Corporate Environmental Accounting
Corporate environmental
accounting focuses on the cost structure and environmental performance of a
company. It is a field that identifies resource use, measures and communicates
costs of a company’s or national economic impact on the environment. Costs
include costs to clean up or remediate contaminated sites, environmental fines,
penalties and taxes, purchase of pollution prevention technologies and waste
management costs.
Corporate environmental
accounting can be further sub-divided into environmental management accounting
and environmental financial accounting.
Environmental Management Accounting
Environmental management
accounting (EMA) is the identification, collection, analysis and use of two
types of information for internal decision making. The first is physical
information on the use, flows and rates of energy, water and materials
(including wastes). The second is monetary information on environment-related
costs, earnings and savings. EMA focuses on making internal business strategy
decisions. EMA is an attempt to integrate best management accounting thinking
and practice with best environmental management thinking and practice.
Environmental Financial Accounting
Environmental financial
accounting is used to provide information needed by external stakeholders on a
company’s financial performance. This type of accounting allows companies to
prepare financial reports for investors, lenders and other interested parties.
References
Abe, M.
(2015). Environmental accounting: Meaning, classifications and importance. Journal
of Environmental Science and Management, 18(2), 27-40.
Antwi, S. K.,
& Osae-Kwapong, I. (2019). Environmental accounting and reporting: A review
of literature. Journal of Environmental and Occupational Science, 8(2),
81-89.
Ayadi, F.
(2017). The role of environmental accounting in sustainable development. Journal
of Economic and Social Development, 4(1), 56-64.
Burritt, R.,
& Schaltegger, S. (2010). Sustainability accounting and reporting: fad or
trend? Accounting, Auditing & Accountability Journal, 23(7), 829-846
Gari, A.,
& Hamzaoui, M. (2016). Environmental accounting: An overview of concepts
and classifications. International Journal of Economics and Management
Engineering, 10(4), 1073-1079.
Hidano, N.,
& Kurisu, K. (2018). Environmental management accounting for decision
making: An empirical study in Japan. Journal of Cleaner Production, 197,
1015-1023.
Joshi, S.,
& Keshari, A. (2020). Environmental accounting: Concept, need and
challenges. International Journal of Research in Commerce and Management,
11(1), 1-6.
Ministry of
Environment (2019). Environmental accounting: A tool for sustainable
development. Retrieved from https://www.env.go.jp/en/earth/ea/intro.html
Schaltegger,
S., & Burritt, R. (2000). Contemporary environmental accounting: issues,
concepts and practice. Sheffield Academic Press.
United
Nations Statistics Division (2019). System of Environmental-Economic
Accounting 2012: Experimental Ecosystem Accounting. Retrieved from https://unstats.un.org/unsd/envaccounting/seeaRev/seeaFlyer.aspx






No comments:
Post a Comment